Have you ever been stumped by a crossword puzzle? Have you ever wished you had the answer to one of its clues without having to do any research or struggle with it? Well, here’s your chance!
In this blog post, we will explore the different aspects of human sight without any aid. From understanding how vision works to looking at various methods of enhancing vision, we’ll cover all things related to seeing and recognizing objects in our environment. Whether you’re a crossword enthusiast or just curious about how humans see without corrective lenses, this blog post has the answers for you!
Visit our page to check some facts about Eyes: celebrities with sanpaku eyes
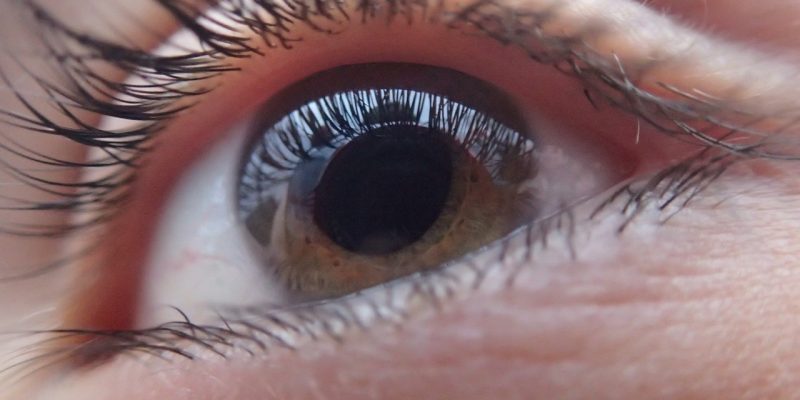
How the human eye works
The human eye is an amazing organ that allows us to see the world around us. It is made up of several parts, each of which plays an important role in allowing us to see.
The cornea is the clear, curved outermost layer of the eye. It protects the rest of the eye and helps to focus light.
The iris is the colored part of the eye that regulates how much light enters the eye. The pupil is the black center of the iris through which light passes.
The lens is a clear structure behind the pupil that helps to focus light on the retina.
The retina is a thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye that contains specialized cells called photoreceptors. These cells convert light into electrical impulses that are sent to the brain via the optic nerve. The brain then interprets these impulses as images.
The different types of vision
There are three types of vision: farsightedness, nearsightedness, and astigmatism. Farsightedness is when you can see distant objects clearly, but close objects appear blurry. Nearsightedness is the opposite – close objects appear clear, but distant objects look blurry. Astigmatism is when your eyes have an irregular curve, which causes light to bend in different directions and makes both near and far objects appear blurred.
There are three types of vision: foveal, peripheral, and night. Foveal vision is the kind we use when looking at something directly; it’s the clearest and most detailed. Peripheral vision is what we use to see things out of the corner of our eye; it’s not as sharp, but it covers a much wider area. Night vision is what we use in low-light conditions; it’s not as clear as foveal or peripheral vision, but it allows us to see in the dark.
What causes poor vision?
There are many possible causes of poor vision, including:
– Refractive error: This is when the eye does not focus light properly, resulting in blurred or distorted vision. Common refractive errors include nearsightedness (difficulty seeing distant objects), farsightedness (difficulty seeing close up) and astigmatism (distorted or blurry vision at all distances).
– Cataracts: A cataract is a clouding of the eye’s lens, which leads to decreased vision. Cataracts usually develop slowly and can be treated with surgery.
– Macular degeneration: This is a deterioration of the macula, the central area of the retina that is responsible for sharp, central vision. Macular degeneration can make everyday activities such as reading or driving difficult or even impossible.
– Glaucoma: This is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, which carries information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated.
You know about a trending category of eyes. If not then click here to know some famous please people’s eyes stories: Celebrities with Sanpaku Eyes
How to improve your sight
There are a number of things you can do to improve your sight without the aid of corrective lenses or surgery. Some simple tips include:
– Taking regular breaks from screens and other close work.
– Giving your eyes a chance to relax and focus on distant objects every 20 minutes.
– Blinking frequently to keep your eyes lubricated.
– Exercising your eyes by following an eye chart or printed sentences with your eyes.
– Adjusting the lighting in your environment to reduce eye strain.
– Wearing sunglasses when outdoors to protect your eyes from harmful UV rays.
There are a number of things you can do to improve your sight without any aid, including:
1. Get plenty of sleep: Sleep is essential for good health and well-being, and it can also help improve your eyesight. Studies have shown that people who get enough sleep are less likely to suffer from eye problems such as dry eye, dark circles under the eyes, and reduced visual acuity.
2. Eat a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help improve your eyesight. Omega-3 fatty acids are especially important for eye health, as they help reduce inflammation and protect the delicate tissue of the eyes.
3. Exercise regularly: Exercise is not only good for your overall health, but it can also help improve your eyesight. Regular exercise helps increase blood flow to the Eyes which helps to keep them healthy and functioning properly.
4. Limit screen time: too much time spent looking at screens (computers, phones, tablets) can lead to digital eye strain, which can cause fatigue, headaches, and even blurry vision. Try to take breaks often when using screens, and make sure to blink frequently to keep your eyes lubricated.
Conclusion
The human sight without any aid crossword is a great way to test your knowledge of the human eye and how it works. It can help you learn more about the mechanics of vision, as well as common words related to visual impairment. With this knowledge, you can understand how we see and how our eyesight changes over time. Take some time with this puzzle to gain a better understanding of your own vision—you may be surprised by what you discover!




















Comments