The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from infections. It is responsible for recognizing and eliminating foreign substances such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi that can cause illness.
Introduction
Our immune system is a complex network of organs, cells, and proteins that work together to protect us from infections.
It is a vital component of our body’s defense mechanism, and without it, we would be susceptible to a wide range of infections and illnesses.
It plays an important role in keeping us healthy by fighting off germs and other foreign bodies that can cause disease. A strong immune system is essential for our overall health.
The Components Of Immune System
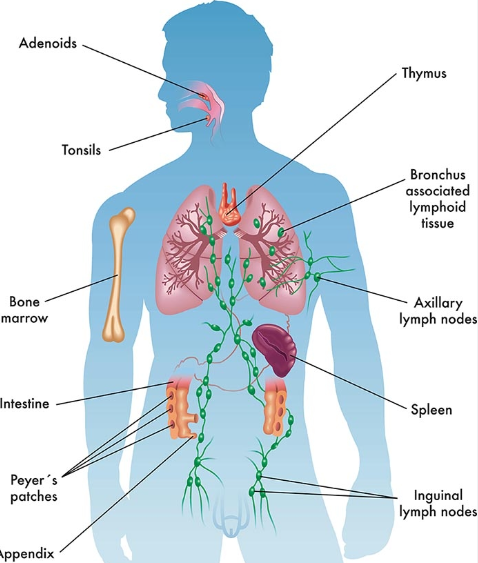
The immune system is made up of several different components, including white blood cells, antibodies, the spleen, the thymus, and the lymphatic system. White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are the main cells that make up the immune system.
They are divided into two main types: B cells and T cells. B cells produce antibodies, which are proteins that help to neutralize or destroy pathogens. T cells, on the other hand, directly attack and destroy infected cells.
The spleen is an organ located in the upper left side of the abdomen that plays a key role in the immune system. It acts as a filter for the blood, removing old and damaged red blood cells and other debris.
The thymus is a gland located in the upper chest that is responsible for the development and maturation of T cells. The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and nodes that helps to transport lymph, a clear fluid that contains white blood cells, throughout the body.
How Does The Immune System Works?
When a pathogen, such as a virus or bacteria, enters the body, it triggers an immune response. White blood cells, such as T cells and B cells, are activated and begin to multiply. The T cells attack and destroy infected cells, while B cells produce antibodies that help to neutralize or destroy the pathogen.
The immune system also has a memory function, which helps it to recognize and quickly respond to pathogens that it has encountered before. This is how vaccines work;
They introduce a harmless version of a pathogen into the body, allowing the immune system to develop a memory of it. If the real pathogen enters the body later, the immune system can quickly recognize and attack it, preventing infection.
Common Conditions That Affect The Immune System
There are several conditions that can affect the immune system’s function, including autoimmune diseases, HIV/AIDS, and cancer.
HIV/AIDS is a viral infection that attacks the immune system, leaving the body vulnerable to other infections. In the advanced stages of AIDS, the immune system is severely weakened, and the person is at risk of developing life-threatening infections such as pneumonia and cancer.
Cancer can also affect the immune system by altering the way the cells in the body grow and divide. Some types of cancer, such as leukemia and lymphoma, originate in the immune system itself.
Conclusion
Understanding how the immune system functions, and the different components that make it up, is crucial to maintaining good health.
The immune system plays a vital role in the body’s defense mechanism, and it is essential to take care of it by eating a healthy diet, getting enough exercise, and getting enough sleep.
It is important to be aware of the common conditions that can affect the immune system and to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect that you may have an immune disorder.


















Comments